- Getting started
- UiPath Agents in Studio Web
- UiPath Coded agents

Agents user guide
Conversational agents
Conversational agents are a class of UiPath agents designed for dynamic, multi-turn, real-time dialogues with users. Unlike autonomous agents that execute tasks from a single prompt, conversational agents interpret and respond to a continuous stream of messages while managing conversation context, tool execution, and human escalations.
Use conversational agents when your automation scenario requires:
- Ongoing clarification or back-and-forth exchange
- Personalized guidance based on user intent
- Seamless human fallback when confidence is low
Conversational agents vs. autonomous agents
| Feature | Conversational agent | Autonomous agent |
|---|---|---|
| Interaction model | Multi-turn, back-and-forth dialogue | Single-turn, task execution based on an initial prompt |
| Primary use case | Real-time user support, interactive information gathering | Executing a task from a defined prompt |
| User input | Continuous chat messages | Single structured prompt |
| Core strength | Maintaining conversation context and handling ambiguity | Executing a plan across tools |
When to use conversational agents
Use conversational agents when your automation involves real-time, context-aware interaction:
- Self-service experiences: Helpdesk support, HR onboarding assistants, IT troubleshooting bots
- Interactive guidance: Multi-step processes, forms, or decision trees
- Contextual conversations: Scenarios where users ask follow-up questions or provide information incrementally
- Natural language interfaces: Querying applications, systems, or knowledge bases conversationally
Use autonomous agents instead when the task can be fully described in a single prompt with all required inputs provided upfront:
- Structured document processing (extracting data from invoices or contracts)
- Automated report generation based on predefined logic
- Summarization or transformation tasks with clear, one-shot requirements
Conversational agents vs. Autopilot for Everyone
How do conversational agents relate to Autopilot for Everyone?
These two experiences work side-by-side:
- Autopilot for Everyone: UiPath's general-purpose assistant, optimized for productivity tasks and interacting with the UiPath platform.
- Conversational agents: Specialized agents you build for specific use cases (such as an HR policy assistant or IT helpdesk bot).
You can access your conversational agents directly from within Autopilot for Everyone, making it a central hub for all your conversational needs.
Our recommendation: We recommend building new conversational use cases on the Conversational Agents platform. It provides a comprehensive design-time experience with built-in evaluation, advanced observability, and full API access.
Conversational agents do not currently support local desktop automation. If your use case requires triggering automations on the user's local machine, this capability is planned for a future release.
The agent lifecycle
Building and operating a conversational agent follows four phases:
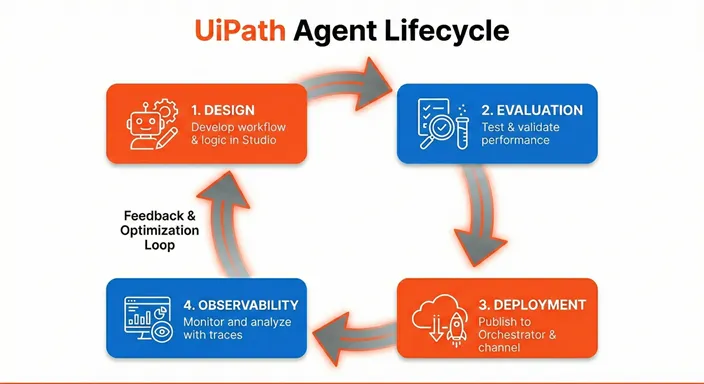
Design
Use Studio Web to define your agent's persona, configure tools, add context grounding for knowledge retrieval, and set up escalation workflows. The low-code designer lets you build agents visually without writing code.
Evaluation
Test your agent using the built-in Debug chat to validate multi-turn interactions. Create evaluation sets from real conversations to measure performance across different scenarios, including single-turn responses and multi-turn dialogue flows.
Deployment
Publish and deploy your agent to Orchestrator and make it available through various channels: Instance Management, Autopilot for Everyone, Microsoft Teams, Slack, or embedded in an iFrame inside third-party apps or UiPath Apps.
Observability
Monitor your agent's performance through Instance Management dashboards, debug using traces, and audit using AI Trust Layer audit. Review trace logs, collect user feedback, and use these insights to iterate on your agent's design—completing the feedback loop.
Next steps
- Getting started: Build your first conversational agent in minutes
- Design: Configure prompts, tools, and contexts
- Licensing: Understand consumption and pricing
- Limitations and FAQ: Current limitations and troubleshooting